How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a question many aspiring pilots ask. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover essential aspects such as understanding airspace regulations, navigating different flight modes, and performing smooth takeoffs and landings. By the end, you’ll possess the knowledge and confidence to confidently take to the skies.
We’ll explore the technology behind drone flight, examining the functions of various controls and the importance of GPS navigation. Furthermore, this guide will provide practical advice on camera operation, image capture techniques, and essential post-flight maintenance procedures to ensure the longevity of your drone. This comprehensive approach ensures you’re equipped to handle any situation, from routine flights to unexpected challenges.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting the drone’s components, verifying battery levels, and confirming compliance with local regulations. Ignoring this step can lead to accidents or malfunctions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection should be performed before every flight. This involves a visual examination of all components to identify any potential issues. The following table provides a structured approach.
| Item | Check | Status (Pass/Fail) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or looseness. | Pass/Fail | Replace damaged propellers immediately. |
| Motors | Check for any visible damage or unusual sounds. | Pass/Fail | Listen for unusual noises during a brief motor test. |
| Battery | Verify sufficient charge and proper connection. | Pass/Fail | Ensure the battery is fully charged and securely connected. |
| Camera | Confirm proper functionality and lens clarity. | Pass/Fail | Test camera functionality by taking a test photo or video. |
| GPS Signal | Ensure a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. | Pass/Fail | Wait for sufficient satellites to lock on. |
| Gimbal | Check for smooth movement and proper alignment. | Pass/Fail | Manually move the gimbal to check for smooth operation. |
| Airframe | Inspect for any damage or cracks in the drone’s body. | Pass/Fail | Check for any signs of impact or wear. |
Understanding Airspace Regulations
Operating a drone requires understanding and adhering to local and national airspace regulations. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines or legal repercussions. Different airspace classifications impose varying restrictions.
- Class G Airspace: Generally unrestricted, but still subject to basic rules like maintaining visual line of sight.
- Class A-E Airspace: These classes are controlled airspace, often requiring prior authorization and specific flight plans. These areas may have height restrictions and other limitations.
- No-Fly Zones: These are designated areas where drone operation is completely prohibited, such as airports, military bases, and prisons.
Safe Flight Conditions Flowchart
A decision-making process is essential to determine safe flight conditions. The following flowchart Artikels a simplified approach:
[Start] –> [Check Weather (Rain, Snow, etc.)] –> [Yes (Unsafe)] –> [End]
[No (Proceed)] –> [Check Wind Speed ( <15 mph)] --> [Yes (Safe)] –> [Proceed to Flight] –> [End]
[No (Unsafe)] –> [End]
Emergency Procedures
Being prepared for emergencies is paramount. Knowing how to react in situations like battery failure or signal loss can prevent accidents and damage.
- Battery Failure: Initiate an immediate, controlled descent using the emergency landing function (if available). If not, gently lower the throttle until landing.
- Loss of Signal: The drone should ideally return to its home point automatically. If this fails, attempt to regain signal or perform an emergency landing.
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
Understanding your drone’s controls and flight modes is essential for safe and effective operation. Different modes cater to varying skill levels and flight scenarios.
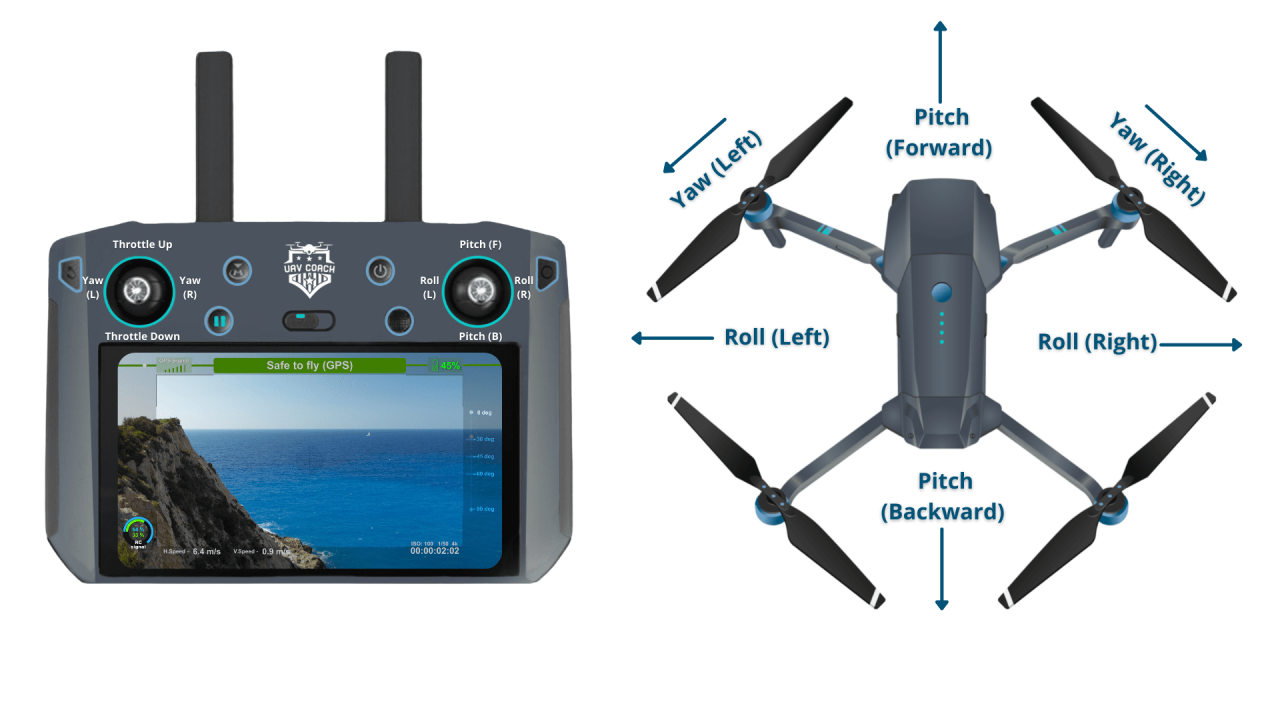
Drone Controller Controls
A typical drone controller uses joysticks and buttons to control various aspects of the drone’s flight. The following table details the common controls and their functions.
| Control | Function | Effect on Drone | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left Stick (Vertical/Horizontal) | Controls altitude and forward/backward movement. | Drone ascends/descends or moves forward/backward. | Pushing the stick up raises the drone; pushing it forward moves it forward. |
| Right Stick (Yaw/Lateral) | Controls rotation (yaw) and left/right movement. | Drone rotates or moves left/right. | Pushing the stick right moves the drone to the right; rotating it clockwise rotates the drone clockwise. |
| Return to Home (RTH) Button | Initiates an automated return to the home point. | Drone automatically flies back to its takeoff location. | Useful in case of signal loss or when you want to end the flight quickly. |
| Camera Control Buttons | Adjusts camera settings like zoom, photo/video recording. | Changes camera settings and captures images or videos. | Pressing the shutter button takes a photo. |
Flight Modes Comparison
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Choosing the right mode depends on your experience and the flight conditions.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness, ideal for learning.
- Sport Mode: Unlocks full speed and responsiveness, suitable for experienced pilots.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for stability and precise positioning, enabling features like RTH.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot, regardless of its position in space.
GPS and Drone Navigation
GPS (Global Positioning System) is crucial for drone navigation and stability. It provides the drone with its location, allowing for features like precise hovering, autonomous flight, and RTH.
Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the compass and other sensors ensures accurate flight and prevents issues like drifting or inaccurate positioning. The specific calibration procedure varies depending on the drone model but usually involves a series of movements as guided by the drone’s software or app.
Taking Off, Flying, and Landing the Drone: How To Operate A Drone
Safe and controlled takeoff, flight, and landing procedures are essential for preventing accidents and ensuring the longevity of your drone. Smooth maneuvers are key to successful drone operation.
Safe Takeoff Procedure

- Perform a pre-flight check.
- Ensure a clear and safe area for takeoff.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition.
- Gently increase the throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Maintain a stable hover before proceeding with flight.
Drone Maneuvering Techniques
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude.
- Turning: Rotating the drone around its vertical axis.
- Forward/Backward/Sideways Movement: Moving the drone in the desired direction.
Controlled Landing Procedure
- Begin descent slowly and steadily.
- Reduce throttle gradually as the drone approaches the ground.
- Maintain a gentle descent rate to prevent a hard landing.
- Power off the drone once it is safely on the ground.
Optimal Flight Path
A typical drone flight path might involve a takeoff, ascent to a desired altitude, lateral movement for capturing shots, a return to the original position, and a controlled descent and landing. This ensures efficient use of battery power and reduces the risk of obstacles.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of most drones. Understanding its settings and how to compose shots will greatly enhance the quality of your aerial photography and videography.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the skies requires practice and a solid understanding of the regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and ensure safe and responsible flight operations.
Safe and efficient drone operation is crucial for both personal enjoyment and professional applications.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Various camera settings influence image quality. Adjusting these settings allows for customization depending on the lighting and desired aesthetic.
- Resolution: Higher resolution means larger image files and more detail, but requires more storage space.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the sensor is exposed to light. Faster speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but can introduce noise.
Adjusting Field of View and Focus
The field of view determines the breadth of the scene captured, while focus affects image sharpness. Adjusting these settings is crucial for framing your shots effectively.
Taking High-Quality Photos and Videos
Taking high-quality aerial shots involves considering factors like lighting, composition, and camera settings. Experimentation and practice are essential to mastering these techniques.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the skies requires a solid grasp of both the technical and regulatory sides; for comprehensive guidance on the latter, you should consult a helpful resource like this guide on how to operate a drone safely and legally. Following these guidelines ensures responsible and compliant drone operation, leading to a safer and more enjoyable flying experience.
Tips for Composing Aerial Shots
- Rule of Thirds: Position key elements along imaginary lines that divide the frame into thirds.
- Leading Lines: Use lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Capture repeating patterns or symmetrical scenes.
- Perspective: Utilize the drone’s unique vantage point to create compelling perspectives.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are crucial for ensuring the longevity and safe operation of your drone. Neglecting these steps can lead to malfunctions and reduced lifespan.
Securing the Drone After Flight
- Power off the drone and controller.
- Remove and store the battery in a safe place.
- Clean the drone’s propellers, body, and camera lens.
- Store the drone in a dry and safe location.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning

Regular cleaning and inspection are vital to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance. This includes checking for loose screws, inspecting propellers for damage, and cleaning the camera lens.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Understanding common malfunctions and their causes helps in troubleshooting and preventing future issues. These could range from simple issues like low battery to more complex problems requiring professional repair.
- Motor Failure: Could be due to physical damage, overheating, or electrical problems.
- GPS Issues: Can be caused by weak signal, interference, or faulty GPS module.
- Battery Problems: May result from improper charging, damage, or aging.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Could stem from physical damage, software glitches, or calibration issues.
Routine Maintenance Schedule, How to operate a drone
A regular maintenance schedule ensures that potential problems are identified and addressed before they escalate. This could involve weekly inspections, monthly cleaning, and quarterly more thorough checks.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | After each flight |
| Cleaning | Weekly |
| Propeller Inspection | Monthly |
| Firmware Update | As needed |
| Comprehensive Check | Quarterly |
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. This guide has provided a framework for safe and efficient drone piloting, emphasizing the importance of pre-flight checks, understanding airspace restrictions, and mastering flight controls. Remember that consistent practice and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for honing your skills and ensuring enjoyable and responsible drone flights.
Embrace the learning process, and soon you’ll be capturing breathtaking aerial perspectives with confidence and skill.
Questions Often Asked
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functionality.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Battery life varies greatly depending on the drone model and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If that fails, try to visually track the drone and attempt to regain control. If it’s unsafe to recover it yourself, report the incident to relevant authorities.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve transported the drone or if you notice erratic behavior.
